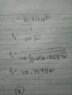Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the resonant frequency of a series RLC circuit with specific parameters, including a leading phase angle of 60° at a frequency of 40 Hz. Participants explore definitions of resonance, impedance characteristics, and the implications of different circuit configurations.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
- Some participants assert that resonance occurs when the total reactance is zero, leading to purely resistive impedance, while others challenge this definition and propose alternative interpretations.
- One participant calculates the resonant frequency to be 81.2 Hz but expresses uncertainty about this result and invites corrections.
- Another participant emphasizes that resonance in a series RLC circuit corresponds to a minimum impedance condition when the inductive reactance equals the capacitive reactance.
- There is a discussion about the definition of resonance, with some suggesting it involves a zero phase difference between voltage and current, while others note that this may not always align with maximum or minimum voltage conditions.
- Participants debate the implications of circuit quality factor (Q) on resonance behavior, particularly in parallel versus series configurations.
- Some participants reference historical texts and definitions, suggesting that interpretations of resonance may vary based on the context and assumptions made about circuit components.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the definition of resonance and its implications for circuit behavior. There is no consensus on the correct interpretation or calculation of resonant frequency, and multiple competing views remain throughout the discussion.
Contextual Notes
Participants note that definitions of resonance may depend on specific circuit configurations and assumptions about component ideality. There are unresolved mathematical steps and varying interpretations of impedance behavior in different circuit types.