MarkFL
Gold Member
MHB
- 13,284
- 12
Here is the question:
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can see my work.
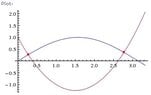
Use Newton's Method to find all roots of the equation sinx= x^2-3x+1 correct to six decimal places.?
I think first thing that I need to do is
let x^2-3x+1-sinx=0
then f(x)=x^2-3x+1-sinx
But I am stuck here...
I don't know how to get the interval and how to get x1
Please please explain how to solve this question for me.
Thank you!
I have posted a link there to this thread so the OP can see my work.