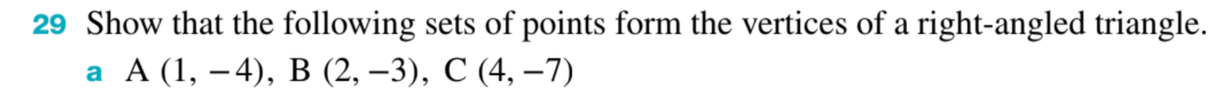Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around demonstrating that a set of three points forms a right-angled triangle. Participants explore various methods including the Pythagorean theorem, slope calculations, and vector analysis.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
Main Points Raised
- One participant suggests using the Pythagorean theorem but finds it unhelpful, seeking alternative suggestions.
- Another participant proposes plotting the points and calculating the slopes of the segments to show that their product is -1, indicating perpendicularity.
- A participant calculates the distances between the points and questions whether the Pythagorean relationship holds for the computed lengths.
- One participant provides slope calculations for the segments and concludes that the product of the slopes confirms the points form a right triangle.
- Another participant introduces a vector approach, demonstrating that the dot product of the vectors is zero, which also indicates perpendicularity.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants present multiple methods to demonstrate the right-angled triangle property, but there is no consensus on a single approach as the definitive solution. Disagreement exists on the effectiveness of the Pythagorean theorem in this context.
Contextual Notes
Some calculations and assumptions regarding the distances and slopes may depend on the specific coordinates of the points, which are not fully detailed in the discussion.