lmf22
- 26
- 0
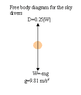
(a) What is the acceleration of two falling sky divers (mass 110.0 kg including parachute) when the upward force of air resistance is equal to one-fourth of their weight?
(b) After popping open the parachute, the divers descend leisurely to the ground at constant speed. What now is the force of air resistance on the sky divers and their parachute?
any help would be great. I don't know where to start.
(b) After popping open the parachute, the divers descend leisurely to the ground at constant speed. What now is the force of air resistance on the sky divers and their parachute?
any help would be great. I don't know where to start.