- #1
chwala
Gold Member
- 2,650
- 351
- Homework Statement
- This is an international past paper question- I have attached the question and the markscheme... the ms was a bit confusing for 2 marks hence my post.
- Relevant Equations
- vectors.
This is an international past paper question- I have attached the question and the markscheme... the ms was a bit confusing for 2 marks hence my post.
Question; interest is on part iii. only

Mark scheme solution;
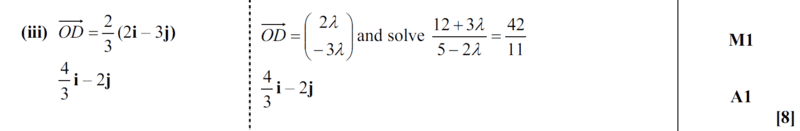 My thinking;
My thinking;
Let
##OD=λOA## Where ##λ## is a scalar.
##OD=λ
\begin{pmatrix}
2 & \\
-3 & \\
\end{pmatrix}##
Let
##DC=κOB## Where ##κ## is a scalar.
##DC=κ
\begin{pmatrix}
11 & \\
42 & \\
\end{pmatrix}##
##OD+DC=OC##
##λ
\begin{pmatrix}
2 & \\
-3 & \\
\end{pmatrix}
+κ
\begin{pmatrix}
11 & \\
42 & \\
\end{pmatrix}
=
\begin{pmatrix}
5 & \\
12 & \\
\end{pmatrix}
##
We end up with the simultaneous equation;
##2λ+11κ=5##
##-3λ+42κ=12##
##39λ=26##
##λ=\dfrac{2}{3}##
therefore,
##OD=\dfrac{2}{3}
\begin{pmatrix}
2 & \\
-3 & \\
\end{pmatrix}=\dfrac{4}{3} i -2j
##
Unless, there is something i have overlooked on the ms... the question ought to have been given more marks...cheers
Your insight highly appreciated.
Question; interest is on part iii. only
Mark scheme solution;
Let
##OD=λOA## Where ##λ## is a scalar.
##OD=λ
\begin{pmatrix}
2 & \\
-3 & \\
\end{pmatrix}##
Let
##DC=κOB## Where ##κ## is a scalar.
##DC=κ
\begin{pmatrix}
11 & \\
42 & \\
\end{pmatrix}##
##OD+DC=OC##
##λ
\begin{pmatrix}
2 & \\
-3 & \\
\end{pmatrix}
+κ
\begin{pmatrix}
11 & \\
42 & \\
\end{pmatrix}
=
\begin{pmatrix}
5 & \\
12 & \\
\end{pmatrix}
##
We end up with the simultaneous equation;
##2λ+11κ=5##
##-3λ+42κ=12##
##39λ=26##
##λ=\dfrac{2}{3}##
therefore,
##OD=\dfrac{2}{3}
\begin{pmatrix}
2 & \\
-3 & \\
\end{pmatrix}=\dfrac{4}{3} i -2j
##
Unless, there is something i have overlooked on the ms... the question ought to have been given more marks...cheers
Your insight highly appreciated.
Last edited: