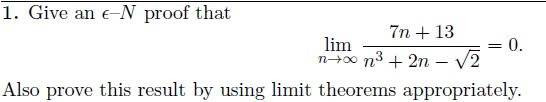SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on solving ϵ-N proofs, specifically simplifying the denominator involving sqrt(2). The key takeaway is that sqrt(2) is a constant and does not affect the limit as n approaches infinity. Participants confirm that to prove the inequality n^3 ≤ n^3 + 2n - sqrt(2), one should eliminate constants in the numerator and denominator to facilitate limit calculations. The limit approaches 0 as n increases, confirming the validity of the proof.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of ϵ-N proofs in calculus
- Familiarity with limit theorems
- Basic knowledge of mathematical induction
- Proficiency in manipulating algebraic expressions
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of ϵ-N proofs in detail
- Learn about limit theorems and their applications
- Explore mathematical induction techniques
- Practice simplifying algebraic expressions for limits
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics, particularly those focusing on calculus and proof techniques, will benefit from this discussion.