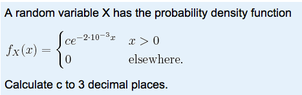SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the integration of a probability density function from 0 to infinity, confirming that the constant \( C \) equals 0.0021. The method used involves integrating the function \( C \, \text{exp}\left(-\frac{2.1x}{1000}\right) \) and setting the result equal to 1. The calculations validate that \( C = \frac{2.1}{1000} \) is indeed correct, establishing the normalization of the distribution.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of probability density functions
- Knowledge of integration techniques in calculus
- Familiarity with exponential functions
- Basic skills in mathematical notation and manipulation
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of probability density functions
- Learn advanced integration techniques, particularly improper integrals
- Explore the applications of exponential functions in statistics
- Investigate normalization conditions for various probability distributions
USEFUL FOR
Students in mathematics or statistics, educators teaching calculus or probability, and professionals working with statistical models and distributions.