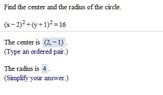Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around understanding the equation of a circle in the form $$(x-h)^2+(y-k)^2=r^2$$, including the implications of changing signs and the meaning of the parameters involved. Participants explore the relationship between the circle's center and its radius, as well as the notation used for the center coordinates.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions whether reversing the signs and squaring is a valid method for solving the equation.
- Another participant explains that the equation represents a circle centered at $(h,k)$ with radius $r$, providing a specific example with coordinates.
- There is a discussion about the meaning of $h$ and $k$, with some participants suggesting they represent the center of the circle and relating it to the Pythagorean theorem.
- One participant expresses confusion about the notation, noting that in other contexts, different letters (like $a$ and $b$) might be used for the center coordinates.
- A later reply confirms that $h$ and $k$ are arbitrary conventions, and that other parameters could be used instead.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the basic structure of the circle's equation and its components, but there is some confusion and disagreement regarding the notation and the implications of changing signs in the equation.
Contextual Notes
Some participants express uncertainty about the notation and its conventions, indicating that the choice of $h$ and $k$ may vary by region or context.