Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the concept of time dilation and age calculation in the context of space travel, particularly focusing on relativistic effects and how they might influence perceived ages of individuals. The conversation includes playful references and speculative reasoning about the implications of these phenomena.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Some participants humorously suggest that space travelers may have their ages misrepresented due to relativistic effects.
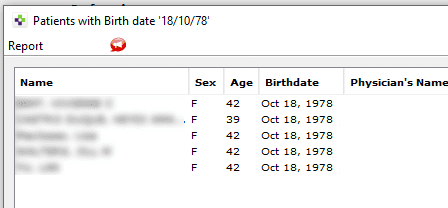
- One participant notes that the ages of individuals are derived programmatically from their birth dates, raising questions about the accuracy of these calculations.
- There is a suggestion that age might only be recalculated on specific dates, such as a birthday, which could lead to discrepancies.
- Another participant introduces the idea that one of the individuals mentioned may have died three years prior, adding a layer of complexity to the discussion.
- Participants engage in playful banter about the implications of time travel and age, with references to specific dates and their significance.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express a mix of playful agreement and speculation, with no clear consensus on the implications of age calculation or the nature of the time travel references. Multiple competing views remain regarding the accuracy and interpretation of the age data.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved assumptions regarding how age is calculated and the implications of relativistic effects on time perception. The discussion includes playful elements that may obscure more serious inquiries into the topic.
Who May Find This Useful
Readers interested in the interplay between relativity, time perception, and age calculation, as well as those who enjoy humorous takes on complex scientific concepts.
 I couldn't see the wood for the trees there.
I couldn't see the wood for the trees there.