- 11,326
- 8,755
Conceptually, negative leap seconds are not much different than positive leap seconds. However, many or most IT systems probably have no provision for negative leap seconds and no testing for that event. Add to our list of time/date headaches; this one not Y2K related.
https://www.timeanddate.com/news/as...ne 29, Earth set,1.50 milliseconds on July 26.
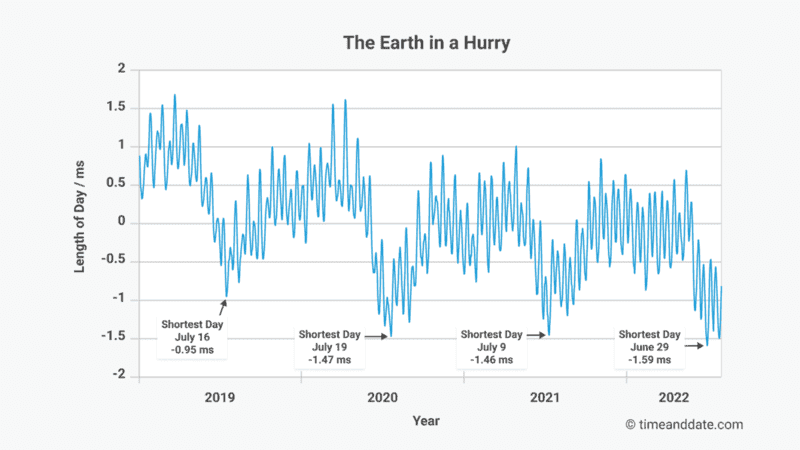
If Earth’s fast rotation continues, it could lead to the introduction of the first-ever negative leap second.
What is causing the current downward trend in the length of the shortest day?
It could be related to processes in Earth’s inner or outer layers, oceans, tides, or even climate. Scientists are not sure, and struggle to make predictions about the length of day more than a year ahead. But there are tentative ideas.
At next week’s annual meeting of the Asia Oceania Geosciences Society (presentation SE05_A009), Leonid Zotov—together with his colleagues Christian Bizouard and Nikolay Sidorenkov—will suggest the current decrease in the length of day could have some relation to the ‘Chandler wobble’.



