SUMMARY
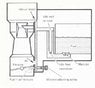
The discussion centers on the differences in airflow dynamics between throttle valves and carburetors. In carburetors, the venturi effect causes a decrease in area and an increase in air velocity, leading to fuel suction. In contrast, throttle valves reduce the quantity of the air-fuel mixture without increasing velocity due to their design, which alters flow characteristics and introduces turbulence. The continuity equation for compressible fluids, represented as ρAV = constant, applies differently in these scenarios, particularly at the throttle valve where flow conditions change significantly.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of fluid dynamics principles, particularly the continuity equation.
- Familiarity with the Bernoulli principle and its application to fluid flow.
- Knowledge of compressible versus incompressible fluid behavior.
- Basic concepts of turbulence and its effects on flow characteristics.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of the continuity equation in compressible fluid dynamics.
- Learn about the Bernoulli equation and its limitations in turbulent flow scenarios.
- Research the effects of turbulence on airflow in throttle valves versus carburetors.
- Examine case studies on airflow dynamics in automotive engineering, focusing on carburetor and throttle valve performance.
USEFUL FOR
Mechanical engineers, automotive engineers, and students studying fluid dynamics who are interested in the practical applications of airflow principles in engine design and performance optimization.