Luke Tan
- 29
- 2
- TL;DR
- Derivation of the transformation rules for the Christoffel symbols.
In Landau Book 2 (Classical Field Theory & Relativity), he mentions that the transformation rules of the christoffel symbols can be gotten by "comparing the laws of transformation of the two sides of the equation governing the covariant derivative"
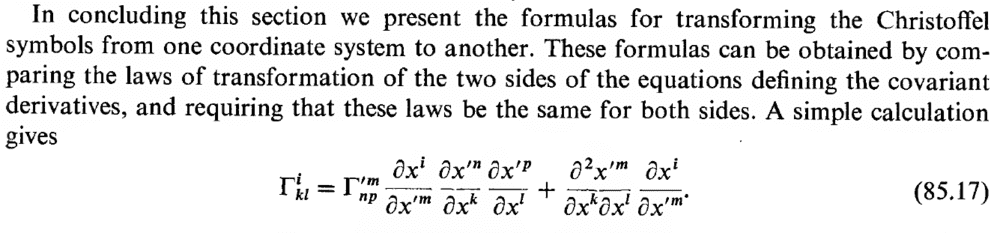
I would believe that by the equations defining the covariant derivative, he means
$$DA^i = (\frac{\partial A^i}{\partial x^l} + \Gamma^i_{kl}A^k)dx^l$$
$$DA_i = (\frac{\partial A_i}{\partial x^k} + \Gamma^k_{il}A_k)dx^l$$
In addition, I would believe that he wants me to use the transformation rules
$$A^i = \frac{\partial x^i}{\partial {x'}^k}{A'}^k$$
$$A_i = \frac{\partial {x'}^k}{\partial x^i}{A'}_k$$However, when attempting to transform the definitions of the covariant derivative from one coordinate system to another, I ran into the following problem - how does the covariant derivative transform? It clearly transforms like a tensor, but does it transform like a covariant tensor, a contravariant tensor, or a mixed one?
So, my questions are:
1. How does a covariant derivative transform? Is it possible to use this to prove the statement that Landau wants to prove?
2. If not, how else would I show this transformation rule for the Christoffel symbols?
I would believe that by the equations defining the covariant derivative, he means
$$DA^i = (\frac{\partial A^i}{\partial x^l} + \Gamma^i_{kl}A^k)dx^l$$
$$DA_i = (\frac{\partial A_i}{\partial x^k} + \Gamma^k_{il}A_k)dx^l$$
In addition, I would believe that he wants me to use the transformation rules
$$A^i = \frac{\partial x^i}{\partial {x'}^k}{A'}^k$$
$$A_i = \frac{\partial {x'}^k}{\partial x^i}{A'}_k$$However, when attempting to transform the definitions of the covariant derivative from one coordinate system to another, I ran into the following problem - how does the covariant derivative transform? It clearly transforms like a tensor, but does it transform like a covariant tensor, a contravariant tensor, or a mixed one?
So, my questions are:
1. How does a covariant derivative transform? Is it possible to use this to prove the statement that Landau wants to prove?
2. If not, how else would I show this transformation rule for the Christoffel symbols?