SUMMARY
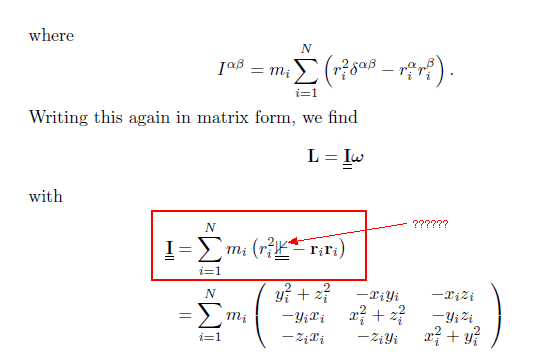
The mysterious symbol in the formal proof of the inertia tensor is identified as the identity matrix, denoted as \mathbb{I}. This conclusion was reached after analyzing its context within the proof and comparing it to the Kronecker delta. The symbol's appearance aligns with the LaTeX (AMS) description of "binary negative entail," but its primary function is confirmed to represent the identity matrix in the context of oscillations and eigenvalues. The discussion highlights the importance of precise symbol rendering in mathematical proofs.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of formal proofs in mathematics
- Familiarity with LaTeX typesetting for mathematical symbols
- Knowledge of the Kronecker delta and its applications
- Basic concepts of linear algebra, particularly identity matrices
NEXT STEPS
- Research LaTeX rendering techniques for mathematical symbols
- Explore the properties and applications of the identity matrix in linear algebra
- Study the Kronecker delta and its role in tensor calculus
- Investigate the use of Lagrangian formulations in physics, particularly in oscillation problems
USEFUL FOR
Mathematicians, physicists, students studying linear algebra and formal proofs, and anyone interested in the nuances of mathematical notation and its implications in theoretical contexts.