Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the acceleration of the universe's expansion, exploring the implications of the Hubble constant and general relativity. Participants examine the relationship between distance, recession velocity, and the changing nature of the Hubble parameter over time.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants question the source of the accelerating force in the universe's expansion, suggesting it may relate to the geometry of general relativity rather than a traditional force.
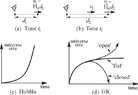
- There is a contention regarding the constancy of the Hubble constant, with some arguing that it is the same at all places in space but changes over time, while others assert that it remains constant at a given cosmic time slice.
- One participant highlights that applying Hubble's law (v = H0d) is valid primarily for nearby galaxies, as the Hubble parameter changes with time, especially for galaxies at larger redshifts.
- Another participant elaborates on how the Hubble parameter decreases over time in a universe not dominated by variable dark energy, affecting the interpretation of recession velocities.
- There is a discussion about the implications of adding components like matter, radiation, and dark energy to the universe, which influence the expansion dynamics differently.
- Some participants express uncertainty about their understanding of the Hubble constant and its relevance across different times and distances.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on the constancy of the Hubble constant or the implications of its variability over time. Multiple competing views remain regarding the interpretation of Hubble's law and the nature of cosmic expansion.
Contextual Notes
Limitations include the dependence on definitions of the Hubble constant and the assumptions about the universe's composition affecting the expansion rate. The discussion also reflects varying interpretations of the implications of general relativity in cosmological contexts.