Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around finding the area of a parallelogram without knowing the height, using given dimensions and angles. Participants explore various methods and formulas applicable to the problem, including the use of trigonometric functions and relationships between the sides and angles of the parallelogram.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Mathematical reasoning
- Homework-related
Main Points Raised
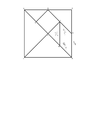
- One participant seeks to find the area of a parallelogram given dimensions of 1/2, 1/2, √2/4, and √2/4, without knowing the height.
- Another participant asks if any angles are known, leading to the revelation that angles E and K are 45 degrees, while angles h and g are 135 degrees.
- A method is proposed to calculate the area using the formula A = a*b*sin(C), where a and b are the lengths of two non-parallel sides and C is the angle between them.
- Clarification is sought regarding which sides to use in the calculation, emphasizing the need for two non-parallel lengths and the angle between them.
- Participants discuss specific calculations, including A = (1/2)(√2/4)sin(135) and alternatives involving different angles and side lengths.
- One participant suggests that the area can also be calculated as the length of one side times the perpendicular distance to the opposite side, leading to a proposed area of 1/8 of a square unit.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants explore multiple approaches to calculating the area, with no consensus on a single method or final answer. Various formulas and interpretations of the dimensions and angles are discussed.
Contextual Notes
Participants rely on specific dimensions and angles, but there may be assumptions about the relationships between these elements that are not fully explored. The discussion does not resolve the potential ambiguity in the application of different formulas.