Discussion Overview
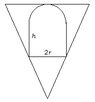
The discussion revolves around determining the optimal dimensions of a cylinder capped with a hemisphere that is inscribed within a cone, specifically focusing on maximizing the volume of this composite shape. The participants explore mathematical relationships and constraints related to the geometry of the cone and the inscribed body.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Exploratory
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- Participants discuss the geometry of a right circular cylinder topped with a hemisphere that fits within a cone of height 15 cm and radius 5 cm.
- There is uncertainty about how to express the height of the cylindrical portion in terms of its radius and other constants.
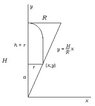
- Some participants propose using coordinate geometry to establish constraints based on the cross-section of the cone and the inscribed body.
- There are multiple attempts to derive equations relating the dimensions of the cylinder and hemisphere to the cone's dimensions, including the use of Thales' theorem.
- One participant suggests that the volume of the body is the sum of the volumes of the cylinder and hemisphere, leading to a composite volume function to maximize.
- Disagreement arises regarding the correct formulation of the relationships between the variables involved, with different participants arriving at different equations and interpretations.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree on the geometric setup of the problem but express differing views on the mathematical relationships and constraints. The discussion remains unresolved, with no consensus on the optimal dimensions or the correct approach to the problem.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the complexity of the problem and the potential need for additional assumptions or clarifications regarding the relationships between the variables. There are unresolved mathematical steps and dependencies on specific definitions that may affect the outcomes.