jayanthd
- 16
- 0
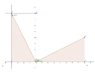
I don't need unit circle proof or proof using trignometric equality. I know those. I am attaching a image. Please read it. It is from the book Plane Trigonometry by S L Loney. See what it says.
I know that angle MOP = angle M'P'O and both triangles formed are congruent, OM' = MP and M'P" = OM and OP' = OP.
Angle P'OM' + angle MOP = 90.
If angle MOP is theta then angle M'P'O is also theta.
Angle OPM = angle P'OM' = 90 - theta because 3 angles of triangle = 180. ( 90 + theta + (90 - theta))
What I don't understand is how is andle MOP = 90 - angle P'OM' and how it is = to angle OP'M'. ( as OP'M' = theta)
http://www.edaboard.com/attachments/92503d1371565911-trigproof.png
The point A in the diagram is wrong. That is my mistake. Point A is to the left of M on x-axis.
There is no error. angle MOP or AOP is theta. AOP' and MOP' are both same. Point A is just to the right of M and A' to the left of M'. My question is how did he calculate
sin(90 + theta) = sin(AOP') = M'P'/OP' = OM/OP. This is giving a problem. M'P'/OP' is cos(theta) in second quardrant.
If we take angle MOP as theta and angle P'OM' as (90 - theta) as sum of the angles should be 90. then angle P'OM' is 90 - theta.
Again if we consider just the triangle in 2nd quadrant then the angle M'P'O is theta and angle P'M'O is 90 and hence the other angle of the triangle is (90 - theta).
M'P'/OP' is sin(90 - theta) of triangle in 2nd quadrant or cos(theta) of triangle in first quadrant.
Then how does he say that M'P'/OP' is sin(90 + theta)?
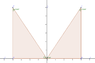
So many people refer the book by S L Loney. I am attaching a new image.
http://www.edaboard.com/attachments/92532d1371636717-trigproof2.png
I know that angle MOP = angle M'P'O and both triangles formed are congruent, OM' = MP and M'P" = OM and OP' = OP.
Angle P'OM' + angle MOP = 90.
If angle MOP is theta then angle M'P'O is also theta.
Angle OPM = angle P'OM' = 90 - theta because 3 angles of triangle = 180. ( 90 + theta + (90 - theta))
What I don't understand is how is andle MOP = 90 - angle P'OM' and how it is = to angle OP'M'. ( as OP'M' = theta)
http://www.edaboard.com/attachments/92503d1371565911-trigproof.png
The point A in the diagram is wrong. That is my mistake. Point A is to the left of M on x-axis.
There is no error. angle MOP or AOP is theta. AOP' and MOP' are both same. Point A is just to the right of M and A' to the left of M'. My question is how did he calculate
sin(90 + theta) = sin(AOP') = M'P'/OP' = OM/OP. This is giving a problem. M'P'/OP' is cos(theta) in second quardrant.
If we take angle MOP as theta and angle P'OM' as (90 - theta) as sum of the angles should be 90. then angle P'OM' is 90 - theta.
Again if we consider just the triangle in 2nd quadrant then the angle M'P'O is theta and angle P'M'O is 90 and hence the other angle of the triangle is (90 - theta).
M'P'/OP' is sin(90 - theta) of triangle in 2nd quadrant or cos(theta) of triangle in first quadrant.
Then how does he say that M'P'/OP' is sin(90 + theta)?
So many people refer the book by S L Loney. I am attaching a new image.
http://www.edaboard.com/attachments/92532d1371636717-trigproof2.png