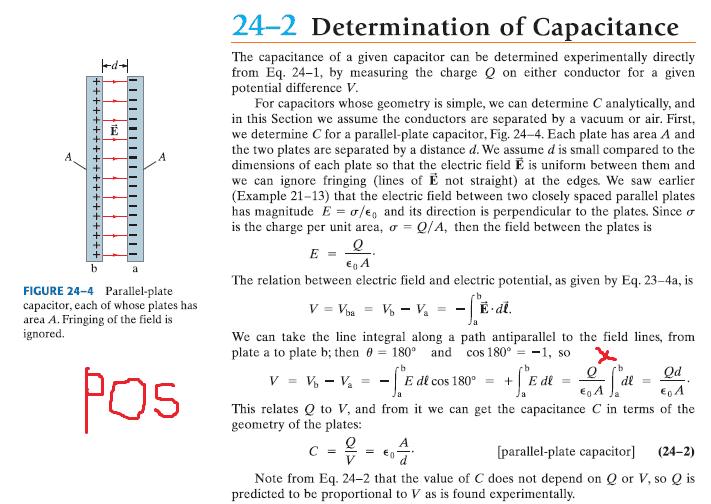
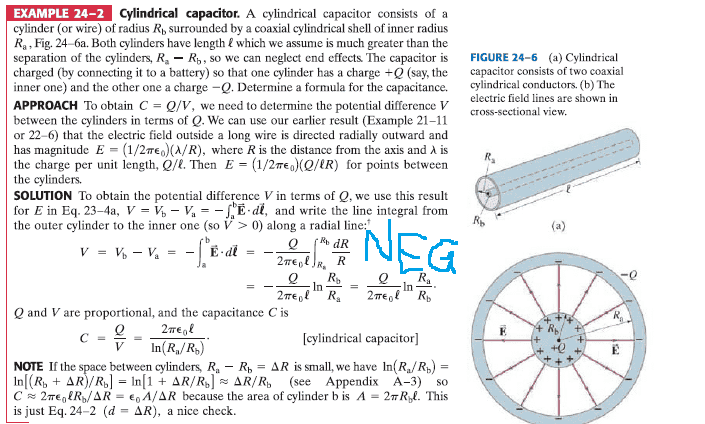
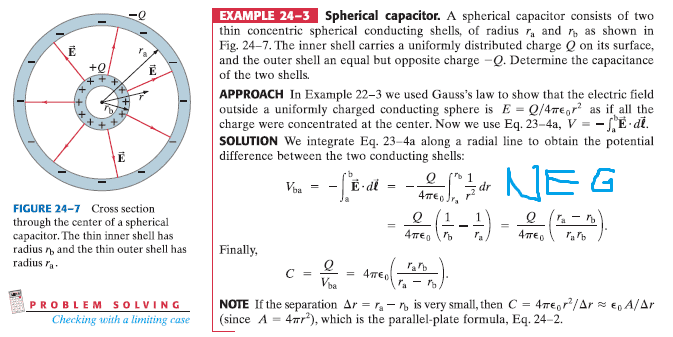
SUMMARY
The discussion clarifies the relationship between the line integral and voltage in the context of electric fields, specifically addressing the apparent contradiction in examples 24-2 and 24-3. The integral is taken anti-parallel to the field lines, resulting in a positive voltage despite the negative integrand. The key takeaway is that the sign of voltage serves primarily as a directional tool, while the magnitude remains the focus. The relationship between the differential path length, dℓ, and the differential resistance, dR, is also highlighted, emphasizing the importance of understanding these variables in electric field calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric field concepts and line integrals
- Familiarity with voltage and potential difference in electrostatics
- Knowledge of calculus, particularly integration techniques
- Basic grasp of vector mathematics, especially dot products
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of voltage from electric fields using line integrals
- Explore the implications of the sign convention in electrostatics
- Investigate the relationship between path length dℓ and resistance dR in circuit analysis
- Learn about the application of the dot product in physics, particularly in electric field calculations
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, electrical engineers, and anyone studying electromagnetism who seeks to deepen their understanding of voltage and electric fields.