SUMMARY
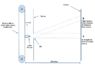
The discussion centers on the trajectory of a laser beam emitted from a moving source at half the speed of light (V=c/2) and its impact on a distant screen. Participants confirm that the laser beam will strike point B on the screen, which is calculated to be 57.7 miles above point A due to the motion of the screen during the time it takes for the light to travel. The analysis includes considerations of both the laser's frame of reference and the screen's frame, employing concepts such as time intervals and relativistic effects. The discussion concludes that regardless of whether diffraction is considered, the primary impact point remains at B.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of special relativity concepts, including time dilation and frame of reference.
- Familiarity with the speed of light (c) and its implications in physics.
- Knowledge of basic trigonometry, particularly the properties of right triangles.
- Concepts of photon behavior and light propagation in different frames of reference.
NEXT STEPS
- Study the implications of special relativity on light propagation, focusing on time dilation effects.
- Learn about the mathematical derivation of Lorentz transformations and their applications.
- Explore the concept of diffraction patterns in laser physics and their experimental setups.
- Investigate the relationship between velocity and light path in various inertial frames.
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, students of physics, and anyone interested in understanding the behavior of light in relativistic contexts, particularly in relation to moving sources and their effects on observation points.