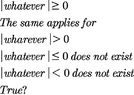Discussion Overview
The discussion centers on the equation \( |x^2 + 4x| = -12 \) and explores why there are no real solutions to this equation. Participants examine the algebraic reasoning behind the absolute value function and its implications for the equation.
Discussion Character
Main Points Raised
- One participant notes that the absolute value of any expression is always greater than or equal to zero, suggesting that \( |x^2 + 4x| \ge 0 \) implies it cannot equal -12.
- Another participant proposes analyzing the equation by considering two cases based on the sign of \( x^2 + 4x \): one where \( x^2 + 4x \ge 0 \) and another where \( x^2 + 4x < 0 \).
- In the first case, they suggest solving \( x^2 + 4x + 12 = 0 \) and recommend checking the discriminant for real solutions.
- In the second case, they propose solving \( -x^2 - 4x + 12 = 0 \) and checking the solutions against the original absolute value equation.
- Another participant succinctly reiterates that since \( |whatever| \ge 0 \), it follows that \( |whatever| \) cannot be less than zero.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants generally agree that there are no real solutions to the equation due to the properties of absolute values, though they explore different algebraic approaches to demonstrate this.
Contextual Notes
Some participants suggest checking the discriminant and the original equation for solutions, indicating that the discussion involves algebraic manipulations that may depend on the definitions and properties of absolute values.