Discussion Overview
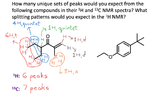
The discussion revolves around the splitting patterns and integrations of red and blue protons in a specific organic compound, focusing on the interpretation of NMR data. Participants explore the reasoning behind the observed patterns and the application of the n + 1 rule in determining splitting.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions why the red and blue protons do not exhibit splitting patterns of "pentet, 6 H" and "octet, 4 H", respectively.
- Another participant reflects on their confusion regarding the professor's designations of "6 H, t" and "4 H, quintet" for the red and blue protons, respectively.
- A participant explains their reasoning, suggesting that the red protons are a triplet due to the adjacent carbons contributing 2 protons, while the blue protons form a quintet based on contributions from two adjacent carbons.
- The explanation includes the application of the n + 1 rule, where the number of adjacent protons influences the splitting pattern.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express confusion and curiosity about the splitting patterns, indicating that there is no clear consensus on the interpretations of the NMR data and the reasoning behind the observed patterns.
Contextual Notes
Participants acknowledge their varying levels of expertise in organic chemistry, which may influence their interpretations and understanding of the problem.