SUMMARY
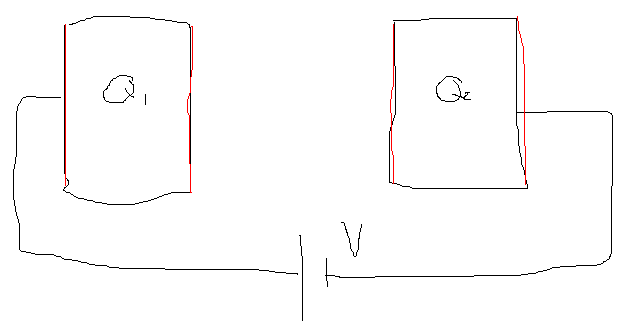
The discussion focuses on the behavior of two charged conductors, Q1 and Q2, when connected to a battery with emf V, forming an ideal parallel plate capacitor. The charges redistribute across four surfaces, with the total charge being Q1 + Q2. The battery maintains a constant potential difference, which influences the charge distribution. The geometry of the conductors is crucial, as it determines the final charge distribution on the surfaces, which can be analyzed using Maxwell's equations if necessary.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric charge and potential difference
- Familiarity with parallel plate capacitors
- Basic knowledge of Maxwell's equations
- Concept of equipotential surfaces in electrical circuits
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of charge distribution in capacitors
- Learn about the implications of ideal conductors in electrical circuits
- Research the application of Maxwell's equations in electrostatics
- Explore the concept of surface charge density in capacitors
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, physicists, and students studying electromagnetism and capacitor design will benefit from this discussion.