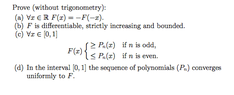Advanced Calculus - Differentiable and Converging Polynomials
- Context: MHB
- Thread starter bradyrsmith31
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the properties of the function $F(x) = \arctan(x)$ and its MacLaurin series expansion. For the interval -1 < x < 1, the series $\frac{1}{1 + x^{2}} = \sum_{n = 0}^{\infty} (-1)^{n} x^{2n}$ converges uniformly, allowing the application of the series integration theorem. The resulting series expansion $F(x) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} (-1)^{n} \frac{x^{2n + 1}}{2n + 1}$ demonstrates that $F(x)$ is an odd function, with alternating signs in its terms, leading to specific inequalities for even and odd n.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of MacLaurin series and their convergence properties
- Familiarity with the concept of odd and even functions
- Knowledge of series integration theorems
- Basic calculus, particularly differentiation and integration of functions
- Study the properties of uniform convergence in series
- Learn about the application of the series integration theorem in calculus
- Explore the implications of odd and even functions in polynomial approximations
- Investigate further examples of MacLaurin series for different functions
Students and educators in advanced calculus, mathematicians focusing on series expansions, and anyone interested in the convergence properties of polynomials and their applications in analysis.
Similar threads
Undergrad
Convergence not defined by any metric
- · Replies 17 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 15 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
Undergrad
Pointwise convergence in Lp space
- · Replies 1 ·
- · Replies 6 ·
- · Replies 4 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 17 ·