sillyquark
- 13
- 0
Hello, this is my first visit to PF. I have a question that I can tell isn't very difficult, but I can't seem get my head around it, maybe i just need to review my text and make an attempt tomorrow.
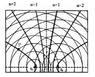
Consider the point P in the following diagram. Analyze this diagram to show that the equation
|P^n S^1-P^2 S^2| = (n-(1/2))(lambda) is valid for this particular location for the point P.
the ^ indicates a subscript
|P^n S^1-P^2 S^2| = (n-(1/2))(lambda)
I haven't made an attempt at a solution, but I am not looking for any answers. If someone could help me understand the problem better, I am sure that I can solve the question.
Homework Statement
Consider the point P in the following diagram. Analyze this diagram to show that the equation
|P^n S^1-P^2 S^2| = (n-(1/2))(lambda) is valid for this particular location for the point P.
the ^ indicates a subscript
Homework Equations
|P^n S^1-P^2 S^2| = (n-(1/2))(lambda)
The Attempt at a Solution
I haven't made an attempt at a solution, but I am not looking for any answers. If someone could help me understand the problem better, I am sure that I can solve the question.
Attachments
Last edited: