Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around calculating the area of a geometric figure, involving a circle and triangles. Participants explore different methods and approaches to find the area, including the use of trapezoids and semi-circles. The conversation includes technical reasoning and attempts to clarify the relationships between various dimensions of the figure.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Technical explanation, Conceptual clarification, Debate/contested, Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
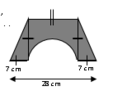
- Susanto presents a problem involving the area of a geometric figure and lists multiple possible area values.
- Some participants inquire about the radius of the circle, with one suggesting it is 14 cm, which is later corrected to indicate it is actually the diameter.
- There is confusion regarding the height of the figure, with suggestions that it is 14 cm based on visual cues.
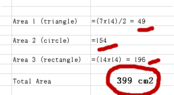
- Participants discuss the components of the area, with one suggesting that the area consists of triangles and a semi-circle, prompting further exploration of how to calculate these areas.
- One participant proposes a formula for the area of a trapezoid and the area of a semi-circle, leading to a derived formula for the total area.
- Another participant points out that the areas should not simply be summed, highlighting the need to account for the number of triangles and the semi-circle's contribution as a subtraction rather than an addition.
- There is mention of a discrepancy in results when using different methods, prompting questions about potential errors in calculations or assumptions.
- Clarifications are made regarding the dimensions used in the calculations, specifically the diameter and bases of the trapezoid.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the correct approach to calculating the area, with some methods being contested and no consensus reached on a single correct method or final answer.
Contextual Notes
Participants express confusion over the relationships between the dimensions and the methods used to calculate the area, indicating potential missing assumptions or misunderstandings in the problem setup.