- #1
FEAnalyst
- 342
- 144
- TL;DR Summary
- How to analyze the telescopic boom of a workshop crane in terms of bending?
Hi,
how can one analyze the telescopic boom of a workshop crane in terms of bending ? Of course the worst case is when the boom is fully extended. Should we treat it as a beam with sudden change of cross-section (or otherwise - with sudden change of flexural stiffness) ? I know that there are different formulas for the deflection of such beam. Where can I find them (or how can I derive them) ? What about the stresses (are they calculated differently too) ?
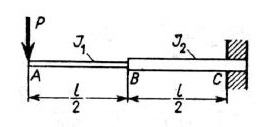
Thanks in advance for your help
how can one analyze the telescopic boom of a workshop crane in terms of bending ? Of course the worst case is when the boom is fully extended. Should we treat it as a beam with sudden change of cross-section (or otherwise - with sudden change of flexural stiffness) ? I know that there are different formulas for the deflection of such beam. Where can I find them (or how can I derive them) ? What about the stresses (are they calculated differently too) ?
Thanks in advance for your help