SUMMARY
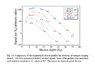
The discussion focuses on modeling bremsstrahlung in scintillators, specifically sodium iodide (NaI) and polystyrene, when high-energy gamma rays interact with recoil electrons. The participants emphasize the importance of accurately capturing energy losses due to bremsstrahlung without directly modeling electron trajectories. Tools like GEANT and MCNP are suggested for proper modeling, while the radiation lengths of materials are discussed to optimize detection efficiency. The conversation highlights the necessity of understanding energy absorption in scintillators to improve measurement accuracy.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of scintillator materials, specifically NaI(Tl) and polystyrene.
- Knowledge of radiation length and its impact on gamma-ray interactions.
- Familiarity with photo-atomic reactions, particularly Compton scattering and pair production.
- Experience with simulation tools like GEANT or MCNP for modeling particle interactions.
NEXT STEPS
- Research the principles of bremsstrahlung and its effects in scintillator detectors.
- Learn how to implement energy loss calculations in GEANT for accurate modeling.
- Investigate the design and optimization of lead-scintillator sandwiches for high-energy photon detection.
- Study the differences in energy resolution and efficiency between various scintillator materials.
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, radiation detection engineers, and researchers involved in high-energy physics experiments, particularly those working with scintillator detectors and gamma-ray spectroscopy.