JudgeA
- 8
- 1
1. Homework Statement
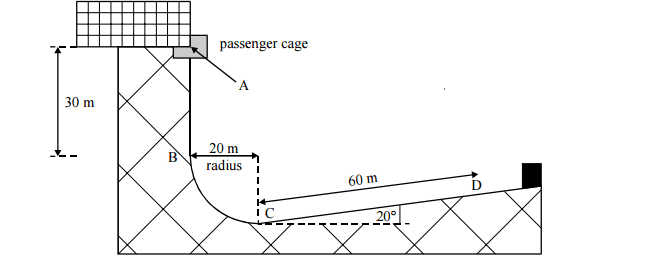
In a theme park ride, a cage containing passengers falls freely a distance of 30 m from A to B and travels in a circular arc of radius 20 m from B to C. Assume that friction is negligible between A and C. Brakes are applied at C after which the cage with its passengers travels 60 m along an upward sloping ramp and comes to rest at D. The track, together with relevant distances, is shown in the diagram. CD makes an angle of 20° with thehorizontal.
(iv) Calculate the average resistive force exerted by the brakes between C and D.
From previous questions I know
Velocity at C = 31.3 m/s²
I know the cage and passengers traveling between C and D has a mass of 620kg
I know the cage gained 1.25*10⁵J of gravitational potential energy between C and D
v²=u²+2as
F=ma
I used v²=u²+2as to find an acceleration of 8 m/s² but didn't know how to proceed from there. If anyone could point me in the right direction that would be very helpful thanks.
In a theme park ride, a cage containing passengers falls freely a distance of 30 m from A to B and travels in a circular arc of radius 20 m from B to C. Assume that friction is negligible between A and C. Brakes are applied at C after which the cage with its passengers travels 60 m along an upward sloping ramp and comes to rest at D. The track, together with relevant distances, is shown in the diagram. CD makes an angle of 20° with thehorizontal.
(iv) Calculate the average resistive force exerted by the brakes between C and D.
From previous questions I know
Velocity at C = 31.3 m/s²
I know the cage and passengers traveling between C and D has a mass of 620kg
I know the cage gained 1.25*10⁵J of gravitational potential energy between C and D
Homework Equations
v²=u²+2as
F=ma
The Attempt at a Solution
I used v²=u²+2as to find an acceleration of 8 m/s² but didn't know how to proceed from there. If anyone could point me in the right direction that would be very helpful thanks.