Discussion Overview
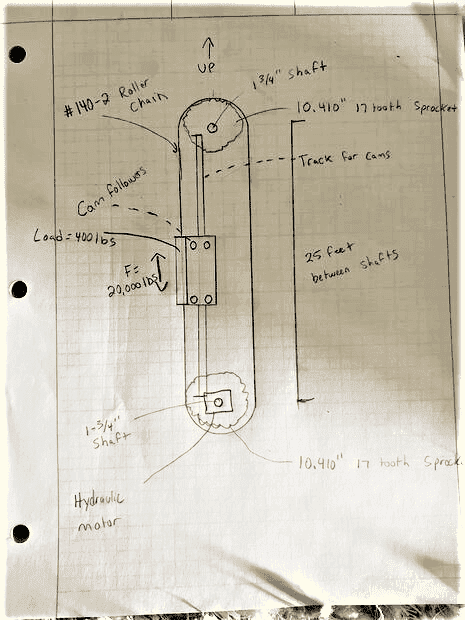
The discussion revolves around determining the torque and RPM required for a hydraulic motor in a two chain sprocket system, specifically for moving a load at a speed of 240 inches per minute. Participants explore the implications of varying loads, friction, and the mechanical setup involved in a water well drilling rig application.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant seeks formulas to calculate the necessary torque and RPM for a hydraulic motor to achieve a specified speed with varying loads.
- Another participant notes that torque requirements depend on the system's acceleration, mass, and friction, which have not been fully specified.
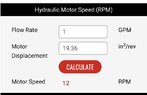
- A formula for RPM based on desired velocity and sprocket diameter is provided, along with a horsepower calculation related to load and speed.
- Concerns are raised about the implications of a vertical setup without a counterweight, suggesting it would significantly increase motor size requirements.
- Clarifications are made regarding the actual load being pushed by the system, indicating that the maximum load is not typically reached, and the system is designed to handle a maximum of 20,000 lbs only in specific scenarios.
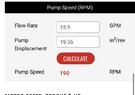
- Participants discuss the challenges of achieving low speeds with high torque pumps and the need for gear reduction to manage speed effectively.
- One participant mentions selecting a hydraulic motor based on available hydraulic flow and pump pressure settings, emphasizing the importance of protecting the chain from exceeding its maximum load.
- Details about a specific hydraulic pump's specifications and how they relate to the system's torque and load capacity are shared.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express varying views on the necessary calculations and considerations for the hydraulic motor setup. While some agree on the importance of torque and RPM calculations, others raise concerns about the vertical configuration and its implications. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the optimal approach to achieve the desired performance.
Contextual Notes
Participants have not fully specified all assumptions regarding load conditions, friction, and acceleration, which may affect the calculations and recommendations. The discussion also highlights the complexity of selecting appropriate hydraulic components based on system requirements.
Who May Find This Useful
Individuals involved in mechanical engineering, hydraulic systems design, or those working on applications related to load movement and torque calculations may find this discussion relevant.