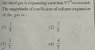SUMMARY
The coefficient of volume expansion (γ) for gases is defined by the equation γ = ∆V/V∆T, where ∆V is the change in volume, V is the initial volume, and ∆T is the change in temperature. The discussion confirms that the coefficient is variable and inversely proportional to temperature, as indicated by the derived relationship ∆V/V∆T = -2/T. The negative sign signifies that volume decreases with increasing temperature in this scenario. Therefore, the correct interpretation is that the coefficient of volume expansion is negative, affirming that as temperature rises, the volume of the gas contracts.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of thermodynamics principles
- Familiarity with the ideal gas law
- Basic calculus for differentiation
- Knowledge of the concept of thermal expansion
NEXT STEPS
- Study the ideal gas law and its implications on gas behavior
- Learn about thermal expansion in solids and liquids
- Explore the mathematical derivation of the coefficient of volume expansion
- Investigate real gas behavior versus ideal gas assumptions
USEFUL FOR
Students studying thermodynamics, physics educators, and professionals in engineering fields focusing on material properties and thermal dynamics.