acm11216
- 1
- 0
Howdy. Long time reader first time posting. Usually try to solve these problems on my own but this one has caused a few sleepness nights already so looking for some insight.
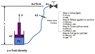
The attached shows a simplified schematic of what I am dealing with. It is basically a hydraulic cylinder with the piston side control line running up to a valve on the "surface" and filled with hydraulic fluid. If I were to apply 500 psi at the surface the pressure below the piston will be 500 psi + head pressure (pgh). For simplicity assume no movement in the piston (resting on shoulder and weight greater than pressure end load from below). Will there be any effect to P2 when closing the surface valve? I don't believe so but unsure the role of hydraulic head in a closed system.
With the surface valve closed I now have a hydraulic lock scenario. However, because the fluid is not perfectly incompressible, I will achieve some movement when pulling up on the hydraulic cylinder. Assuming no seal leakage, this movement will be maxed out when the pressure drops to 0 psi. I can use bulk modulus of elasticity for the control fluid to relate volume and pressure changes but how do I apply in this case? Is the maximum pressure drop 500 psi, 500 psi + head pressure, or somewhere in between? In the long run I am working to determine piston stroke vs F and P1/P2 relation.
Any insight would be helpful. Thanks in advance for even reading
The attached shows a simplified schematic of what I am dealing with. It is basically a hydraulic cylinder with the piston side control line running up to a valve on the "surface" and filled with hydraulic fluid. If I were to apply 500 psi at the surface the pressure below the piston will be 500 psi + head pressure (pgh). For simplicity assume no movement in the piston (resting on shoulder and weight greater than pressure end load from below). Will there be any effect to P2 when closing the surface valve? I don't believe so but unsure the role of hydraulic head in a closed system.
With the surface valve closed I now have a hydraulic lock scenario. However, because the fluid is not perfectly incompressible, I will achieve some movement when pulling up on the hydraulic cylinder. Assuming no seal leakage, this movement will be maxed out when the pressure drops to 0 psi. I can use bulk modulus of elasticity for the control fluid to relate volume and pressure changes but how do I apply in this case? Is the maximum pressure drop 500 psi, 500 psi + head pressure, or somewhere in between? In the long run I am working to determine piston stroke vs F and P1/P2 relation.
Any insight would be helpful. Thanks in advance for even reading