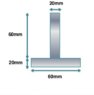
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on calculating the moment of inertia (MoI) for a T-section, specifically whether to find it with respect to both the x and y axes or just the centroidal axis. Participants clarify that the MoI should be calculated about the centroidal axis, which is an axis passing through the centroid of the shape. The perpendicular axis theorem is highlighted as a useful method for determining the MoI about an axis normal to the plane by summing the MoIs about two perpendicular axes in the plane. The consensus is to report the MoI about the centroidal axis without combining them into a polar second moment of area unless specified.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of moment of inertia (MoI) concepts
- Familiarity with centroidal axes and their significance
- Knowledge of the perpendicular axis theorem
- Basic principles of mechanics of solids
NEXT STEPS
- Study the application of the perpendicular axis theorem in detail
- Learn how to calculate moment of inertia for various geometric shapes
- Explore the differences between centroidal and non-centroidal axes
- Investigate the implications of polar moments of inertia in structural analysis
USEFUL FOR
Engineering students, mechanical engineers, and anyone involved in structural analysis or mechanics of materials will benefit from this discussion on calculating the moment of inertia for complex shapes like T-sections.