lorenz0
- 151
- 28
- Homework Statement
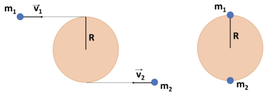
- A disk of mass ##m=10kg## e raggio ##R=0.5 m## is initially at rest on a horizontal plane without friction. Two point masses ##m_1=5kg## and ##m_2=1kg## move with speed ##v_1=2m/s## and ##v_2=4m/s## the first from left to right and the second from right to left. At a certain istant ##m_1## and ##m_2## hit the disk in a completely inelastic collision.
Find: 1) Velocity of the center of mass after the collision; 2) Angular velocity of the disk after the collision; 3) If the disk had a rod passing through its center of mass and perpendicular to the the disk find its angular velocity after the collision and the impulse given by the rod in the collision; 4) If now the rod where to apply a braking torque ##\tau=-0.2 N\cdot m## to the disk, after how many turns would the disk (with the two masses) stop?
- Relevant Equations
- ##\vec{L}=\vec{r}\times\vec{p}=I\vec{\omega}, \omega_f^2=\omega_i^2+2\alpha\Delta\theta##
1) By conservation of linear momentum: ##m_1 v_1-m_2v_2=(m+m_1+m_2)v_{cm}\Rightarrow v_{cm}=\frac{m_1}{m+m_1+m_2}v_1-\frac{m_2}{m+m_1+m_2}v_2=\frac{3}{8}\frac{m}{s}##;
2) By conservation of angular momentum: ##-Rm_1v_1-Rm_2v_2=I_{total}\omega=(I_{disk}+m_1R^2+m_2R^2)\omega## so
##-(m_1v_1+m_2v_2)R=(\frac{1}{2}mR^2+m_1R^2+m_2R^2)\omega\Rightarrow\omega=-\frac{m_1v_1+m_2v_2}{\frac{m}{2}+m_1+m_2}=-\frac{14}{11}\frac{rad}{s}##;
3) To find the impulse given by the rod we can use the impulse theorem so ##I=(m+m_1+m_2)v_{cm}=16\cdot\frac{3}{8}\frac{kg\cdot m}{s}=6 \frac{kg\cdot m}{s}##. Now, to find the angular velocity in this case I would do the same analysis as in (2) and say the angular velocity is thus the same but I am not sure so I would appreciate a comment about how to think about this case.
4) ##\omega_f^2=\omega_i^2+2\alpha\Delta\theta## which in our case gives ##0=\omega_i^2-2\frac{|\tau|}{I_{tot}}\Delta\theta\Rightarrow\Delta\theta=\frac{I_{tot}\omega_i^2}{2|\tau|}\omega_i^2=\frac{(\frac{1}{2})mR^2+m_1R^2+m_2R^2)\omega_i^2}{2|\tau|}\omega_i^2=\frac{(5+5+1)(\frac{1}{2})^2}{2\frac{1}{5}}(\frac{14}{11})^2 rad=\frac{245}{22} rad## so the number of turns is ##n_{turns}=\frac{\frac{245}{22}}{2\pi}=\frac{245}{44\pi}##.
2) By conservation of angular momentum: ##-Rm_1v_1-Rm_2v_2=I_{total}\omega=(I_{disk}+m_1R^2+m_2R^2)\omega## so
##-(m_1v_1+m_2v_2)R=(\frac{1}{2}mR^2+m_1R^2+m_2R^2)\omega\Rightarrow\omega=-\frac{m_1v_1+m_2v_2}{\frac{m}{2}+m_1+m_2}=-\frac{14}{11}\frac{rad}{s}##;
3) To find the impulse given by the rod we can use the impulse theorem so ##I=(m+m_1+m_2)v_{cm}=16\cdot\frac{3}{8}\frac{kg\cdot m}{s}=6 \frac{kg\cdot m}{s}##. Now, to find the angular velocity in this case I would do the same analysis as in (2) and say the angular velocity is thus the same but I am not sure so I would appreciate a comment about how to think about this case.
4) ##\omega_f^2=\omega_i^2+2\alpha\Delta\theta## which in our case gives ##0=\omega_i^2-2\frac{|\tau|}{I_{tot}}\Delta\theta\Rightarrow\Delta\theta=\frac{I_{tot}\omega_i^2}{2|\tau|}\omega_i^2=\frac{(\frac{1}{2})mR^2+m_1R^2+m_2R^2)\omega_i^2}{2|\tau|}\omega_i^2=\frac{(5+5+1)(\frac{1}{2})^2}{2\frac{1}{5}}(\frac{14}{11})^2 rad=\frac{245}{22} rad## so the number of turns is ##n_{turns}=\frac{\frac{245}{22}}{2\pi}=\frac{245}{44\pi}##.
Attachments
Last edited: