crick
- 39
- 4
The potential energy associated to the interaction between nucleons has its minimum (point of equilibrium) at ##r\sim 0.7 fm##, as showed in the following graph:
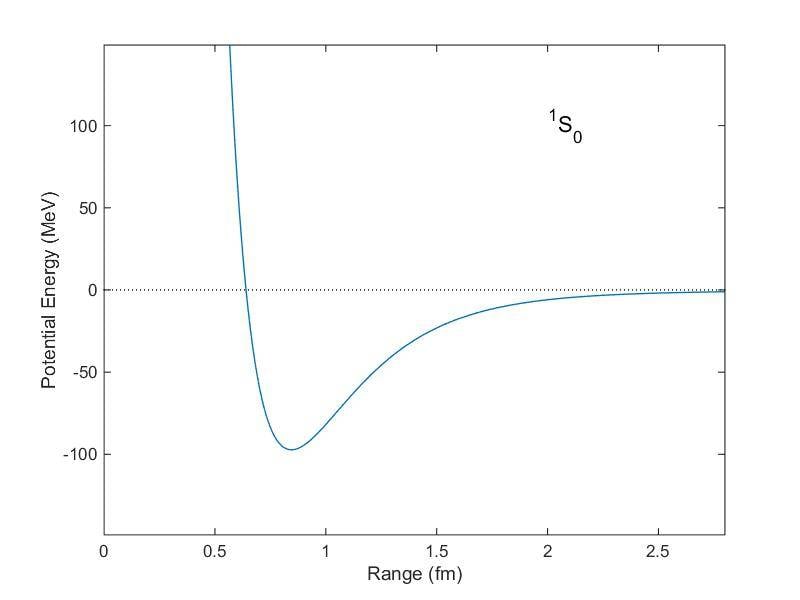
Nevertheless, there are two facts that are, apparently, in contrast with this:
- The average distance between nucleons is ##\sim 1-2 fm##
- The average nucleon density is ##\sim 0.17\,\,\ \mathrm{nucleons /fm^3}##
(These two are related because from the second follows a volume of ##\sim 6 fm^2## per nucleon which is in agreement with the average distance between nucleons)
So why is the average distance between nucleons usually greater that the ##0.7 fm## where the potential energy is minimum?
I'm aware that the "dimension" of nucleon is ##\sim 1 fm##. But is this the reason why the distance between two of them cannot be much less?
Nevertheless, there are two facts that are, apparently, in contrast with this:
- The average distance between nucleons is ##\sim 1-2 fm##
- The average nucleon density is ##\sim 0.17\,\,\ \mathrm{nucleons /fm^3}##
(These two are related because from the second follows a volume of ##\sim 6 fm^2## per nucleon which is in agreement with the average distance between nucleons)
So why is the average distance between nucleons usually greater that the ##0.7 fm## where the potential energy is minimum?
I'm aware that the "dimension" of nucleon is ##\sim 1 fm##. But is this the reason why the distance between two of them cannot be much less?