SUMMARY
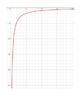
The discussion centers on the behavior of electrical potential energy (PE) between charged particles, specifically addressing why PE decreases as the distance between opposite charges increases. The formula for electrical potential energy is given as U = k(q1q2)/r, where k is a constant. Participants clarify that while gravitational potential energy increases with height (U = mgh), electrical potential energy behaves differently due to the signs of the charges involved. For opposite charges, the potential energy is negative and approaches zero as distance increases, contrasting with the positive potential energy of like charges.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electrical potential energy, specifically U = k(q1q2)/r
- Familiarity with gravitational potential energy, U = mgh
- Basic knowledge of positive and negative charges in electrostatics
- Algebraic manipulation of equations involving real numbers
NEXT STEPS
- Study the concept of electric fields and their relationship to potential energy
- Explore the implications of charge signs on potential energy calculations
- Learn about the differences between gravitational and electrical potential energy
- Investigate the concept of potential energy approaching zero at infinity for opposite charges
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, educators explaining electrostatics, and anyone seeking to understand the nuances of electrical potential energy in relation to charged particles.