Bolter
- 262
- 31
- Homework Statement
- See question below
- Relevant Equations
- None
Hey everyone!
So I have attempted this Q which is shown below

I had a go at all the parts and I think they are right
but I'm not so sure on what answer to give for c)iii, I mentioned about the ratio of protons to neutrons but I'm not sure if that is necessary over here?
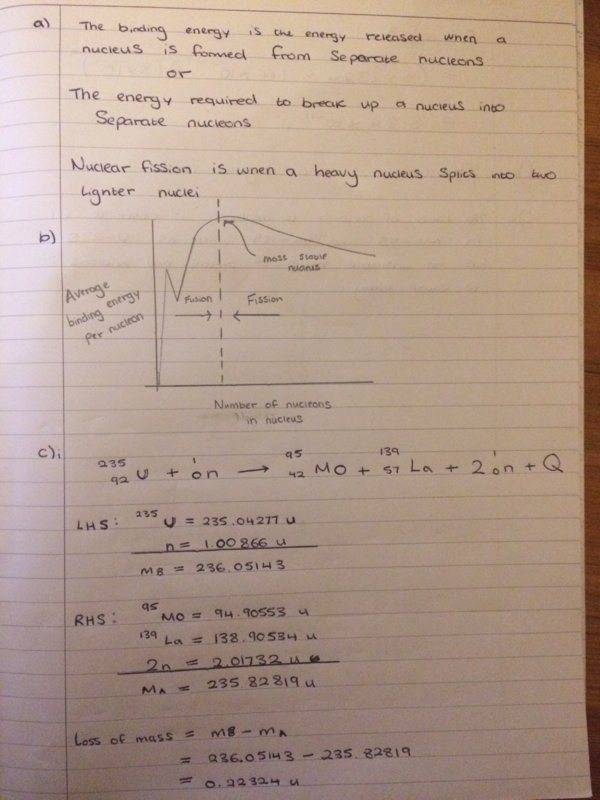
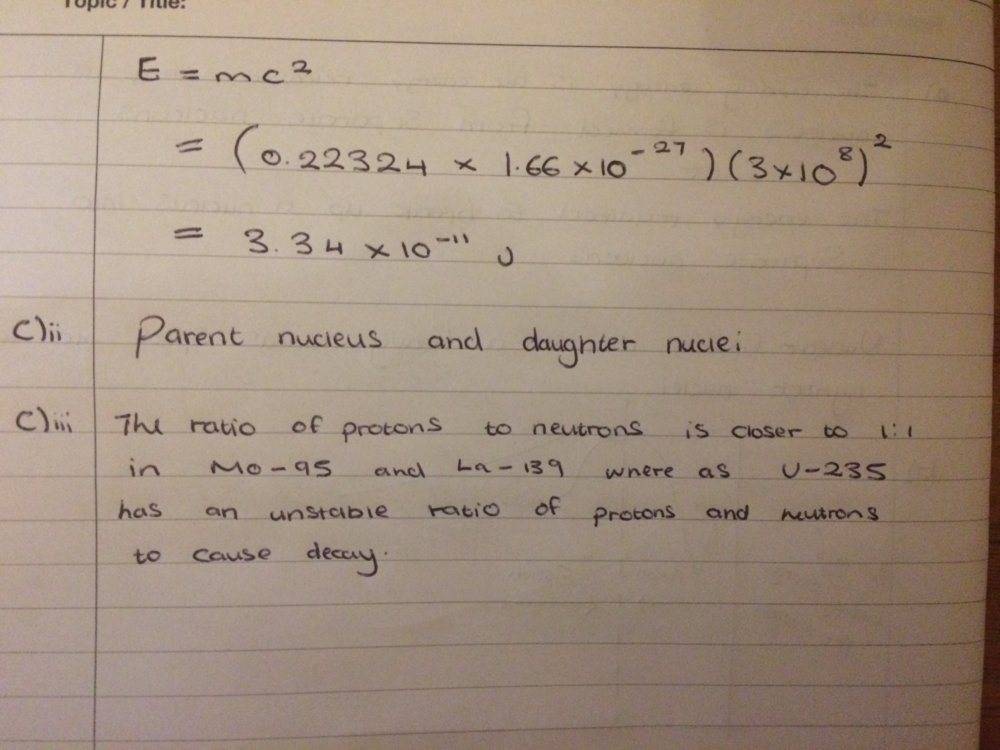
Any help would be grateful! Thanks
So I have attempted this Q which is shown below
I had a go at all the parts and I think they are right
but I'm not so sure on what answer to give for c)iii, I mentioned about the ratio of protons to neutrons but I'm not sure if that is necessary over here?
Any help would be grateful! Thanks