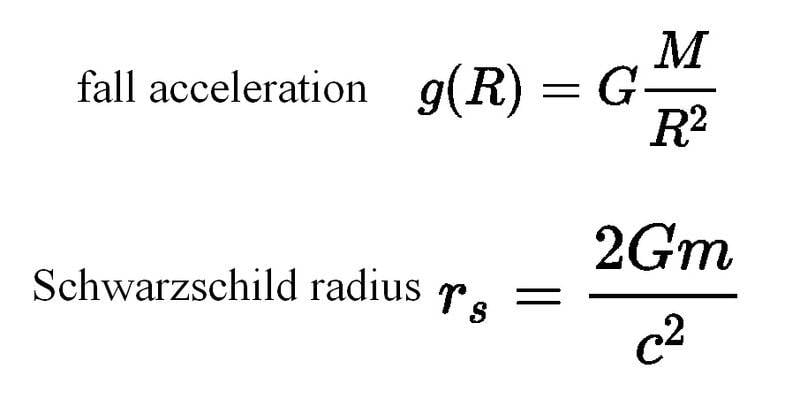Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the experience of falling into a massive black hole, particularly focusing on the implications of the Schwarzschild radius and the effects of acceleration and tidal forces. Participants explore the nuances of gravitational effects near black holes, including whether one would notice anything special upon crossing the event horizon.
Discussion Character
- Debate/contested
- Technical explanation
- Conceptual clarification
Main Points Raised
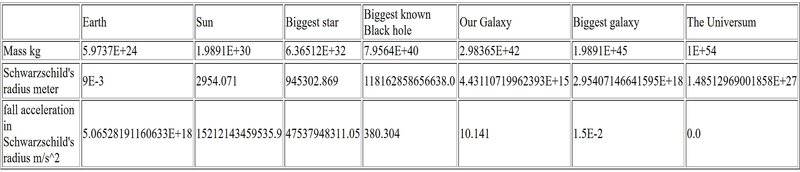
- Some participants suggest that the fall acceleration at the Schwarzschild radius is weaker for more massive black holes, leading to the idea that one might not notice anything special when crossing the event horizon.
- Others challenge the interpretation of fall acceleration, arguing that it is a technical concept and that proper acceleration experienced by an object differs from the force exerted by an observer at infinity.
- One participant emphasizes that at the Schwarzschild radius, hovering is impossible, which complicates the notion of fall acceleration.
- Another viewpoint is presented that tidal forces are more significant than fall acceleration, with larger black holes exhibiting smaller tidal forces, thus reducing the sensation of spaghettification.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the relevance of fall acceleration versus tidal forces, indicating a lack of consensus on the primary factors affecting the experience of falling into a black hole.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved technical distinctions regarding the definitions of fall acceleration and proper acceleration, as well as the implications of tidal forces in the context of black hole physics.