Dustinsfl
- 2,217
- 5
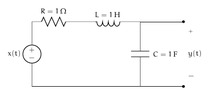
Determine \(H(s)\) and specify its region of convergence. Your answer should be consistent with the fact that the system is causal and stable.
In order to find \(H(s)\), we need to find \(X(s)\) and \(Y(s)\).
\begin{align*}
x(t) &= Ri + L\frac{di}{dt} + \frac{1}{C}\int i(t)dt\\
X(s) &= \mathcal{L}\bigg\{i + \frac{di}{dt} + \int i(t)dt\bigg\}\\
&= I(s) + sI(s) - I(0) + \frac{1}{s}I(s)\\
&= I(s)\bigg(1 + s + \frac{1}{s}\bigg)\\
y(t) &= \frac{1}{C}\int i(t)dt\\
&= \mathcal{L}\bigg\{\int i(t)dt\bigg\}\\
&= \frac{1}{s}I(s)\\
H(s) &= \frac{\frac{1}{s}}{1 + s + \frac{1}{s}}\\
&= \frac{1}{s^2 + s + 1}
\end{align*}
View attachment 2097
What is a causal system?
For convergece, \(\text{Re} \ \{s\} < -\frac{1}{2}\) since the inverse Laplace of H is
\[
\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}e^{-\frac{1}{2}t}\sin\Big(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}t\Big).
\]
In order to find \(H(s)\), we need to find \(X(s)\) and \(Y(s)\).
\begin{align*}
x(t) &= Ri + L\frac{di}{dt} + \frac{1}{C}\int i(t)dt\\
X(s) &= \mathcal{L}\bigg\{i + \frac{di}{dt} + \int i(t)dt\bigg\}\\
&= I(s) + sI(s) - I(0) + \frac{1}{s}I(s)\\
&= I(s)\bigg(1 + s + \frac{1}{s}\bigg)\\
y(t) &= \frac{1}{C}\int i(t)dt\\
&= \mathcal{L}\bigg\{\int i(t)dt\bigg\}\\
&= \frac{1}{s}I(s)\\
H(s) &= \frac{\frac{1}{s}}{1 + s + \frac{1}{s}}\\
&= \frac{1}{s^2 + s + 1}
\end{align*}
View attachment 2097
What is a causal system?
For convergece, \(\text{Re} \ \{s\} < -\frac{1}{2}\) since the inverse Laplace of H is
\[
\frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}e^{-\frac{1}{2}t}\sin\Big(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}t\Big).
\]