SUMMARY
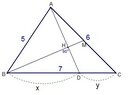
The discussion focuses on finding the ratio of segments $\overline{BD}$ to $\overline{CD}$ in triangle $\triangle ABC$ where $\overline{AB}=5$, $\overline{AC}=6$, and $\overline{BC}=7$. The point $M$ is defined as the midpoint of $\overline{AC}$, and point $D$ lies on $\overline{BC}$ such that $\overline{AD}$ is perpendicular to $\overline{BM}$. The conclusion reached is that the ratio $\overline{BD}:\overline{CD}$ is 5:2.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of triangle properties and segment ratios
- Knowledge of coordinate geometry and midpoints
- Familiarity with perpendicular lines and their implications in geometry
- Basic skills in solving geometric problems involving triangles
NEXT STEPS
- Study the properties of triangle medians and centroids
- Learn about the use of coordinate geometry to solve geometric problems
- Explore the concept of similar triangles and their ratios
- Investigate the application of the Pythagorean theorem in triangle problems
USEFUL FOR
Students studying geometry, mathematics educators, and anyone interested in solving geometric problems involving triangles and segment ratios.