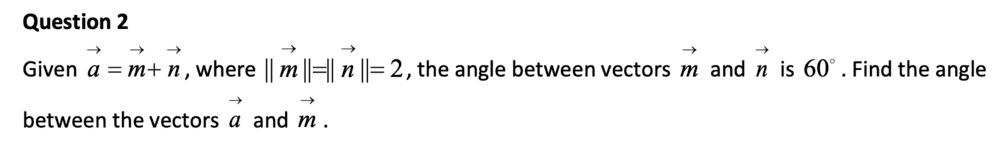
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on calculating the angle between vectors a and m, given the magnitudes of vectors m and n, and the angle between m and n, which is 60 degrees. The initial geometric approach suggested an angle of 30 degrees; however, the correct angle is 54.7 degrees. The formula provided for calculating the angle is based on the cosine of the angle, expressed as $$\cos \theta= \frac {\vec a . \vec m}{||\vec a|| ||\vec m||}$$, indicating the need for precise vector calculations to arrive at the correct answer.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vector mathematics
- Familiarity with the cosine rule in trigonometry
- Knowledge of dot product calculations
- Basic geometry concepts related to angles and magnitudes
NEXT STEPS
- Study vector dot product and its applications in angle calculations
- Learn about the cosine rule and its use in determining angles in triangles
- Explore vector magnitude calculations and their significance
- Practice solving problems involving angles between vectors using geometric and algebraic methods
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in mathematics, physics, and engineering who are working with vector analysis and need to accurately determine angles between vectors.