anonymous812
- 10
- 0
Homework Statement
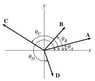
Four vectors A, B, C, and D are shown (not to scale). Vector A has magnitude 20.0 and acts at an angle of 12.9 degrees with respect to the positive x axis. Vector B has magnitude 15.0 and acts at an angle of 55.7 degrees with respect to the positive x axis. Vector C has magnitude 31.5 and acts at an angle of 146.5 degrees with respect to the positive x axis. Vector D has magnitude 13.0 and acts at an angle of 296.4 degrees with respect to the positive x axis.
Question: What are the magnitude and direction of the resultant vector, R, when the parallelogram law is applied to A and B?
Homework Equations
Law of Sines and Law of Cosines..
A/sina=B/sinb=C/sinc
C=sqrt(A^2+B^2-2ABcos(c)
The Attempt at a Solution
I solved for The resultant vector and got 32.6 N... R=sqrt(20^2 +15^2-2(20*15*cos(137.2)))
Then I used law of sines to find the direction and got 52.5 degrees.
Apparently, I'm wrong. I recalculated all the angles not given and they seem to be right, but my end result ends up being wrong. Any tips?
Thank you!