SUMMARY
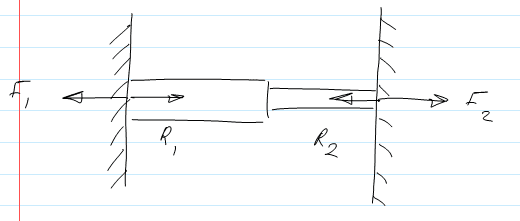
The discussion centers on the forces generated by a linear actuator wedged between two solid walls, exerting an outward force of 10N. Participants concluded that in a state of equilibrium, the forces F1 and F2, as well as the reaction forces R1 and R2, must equal 5N each. This is due to the balance of forces, where the total compressive force (20N) must equal the total expansive force (10N) produced by the actuator. Thus, the correct magnitudes of the forces are established as F1 = F2 = R1 = R2 = 5N.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Newton's laws of motion
- Basic principles of static equilibrium
- Knowledge of force vectors and their components
- Familiarity with linear actuators and their applications
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of static equilibrium in mechanical systems
- Learn about force distribution in structures and materials
- Explore the mechanics of linear actuators and their specifications
- Investigate real-world applications of linear actuators in engineering
USEFUL FOR
Mechanical engineers, physics students, and anyone involved in the design and analysis of systems utilizing linear actuators will benefit from this discussion.