darkchild
- 153
- 0
Homework Statement
This is from a Physics GRE practice test:
An 8-cm-diameter by 8-cm-long NaI(Tl) detector detects gamma rays of a specific energy from a point source of radioactivity. When the source is placed just next to the detector at the center of the circular face, 50% of all emitted gamma rays at that energy are detected. If the detector is moved to 1 meter away, the fraction of detected gamma rays drops to
(A)10^{-4}
(B)2 X 10^{-4}
(C)4 X 10^{-4}
(D)8 \pi X 10^{-4}
(E)16 \pi X 10^{-4}
Homework Equations
None are given, and I don't know if there are any in particular I'm supposed to know.
The Attempt at a Solution
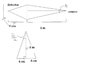
Please see the attached jpeg image for how I set my figure up. It shows the detector from the side (basically an 8cm long circular cone). I assumed that the source was still lined up with the center of the detector, i.e., just moved 1 m straight backwards. First, I decided that, when immediately adjacent to the source, the detector was privy to gamma rays emitted at any angle such that - \pi < \theta < \pi (for a total range of 180 degrees) where the angle is measured from the straight line runs from the source to the center of the detector. At 1 m distance, the magnitude of this unknown range is the variable \theta.
Using lines from the source to the edges of the detector, I constructed the triangle that is in blue. Using the right triangle,
2 \arctan (\frac{4 cm}{100 cm}) = \theta.
I expressed this as a fraction of the total angular range of emitted gamma rays using a proportion: A 180 degree range of gamma rays corresponded to 50% of the total emitted, and so:
\frac{\pi}{.5} = \frac{\theta}{x}
where x is my final answer: 0.01273 which is way off; the answer is C.
I've never even seen a problem like this before, so I'm not sure if I'm doing it correctly.