Bastian1978
- 4
- 0
Hi all,
I have been reading the book "Computational Dynamics" by Ahmed Shabana, and have a few questions.
The book talks about creating "free-body diagrams" for constrained rigid multibody dynamics problems.
I have attached two examples:
The first is a "pendulum with a moving base":

which is described in the book as:
"Body 1 is a slider block that has a specified motion defined by the function z(t). Body 2 is a uniform slender rod that has mass m2, mass moment of inertia about its centre of mass J2, and length l. The rod that is subjected to the external moment M2 is connected to the sliding block by a pin joint at O."
The second,
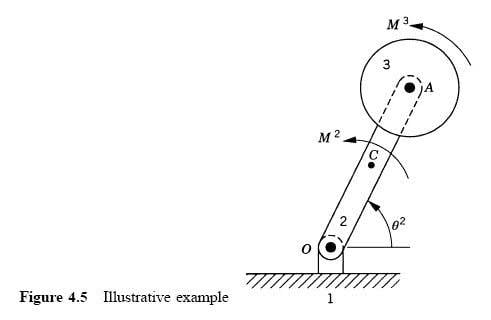
is described in the book as:
"The system consists of the ground denoted as body 1, a rod OA denoted as body 2, and a disk denoted as body 3. The rod is connected to the ground by a pin joint at O, while the disk is connected to the rod by a pin joint at A. The rod is assumed to be uniform and its length is l."
I have also attached the book's free-body diagrams for these two examples.
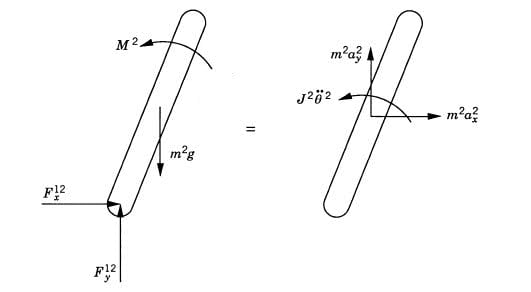

I'm unclear about how the free-body diagrams are constructed (and it is assumed knowledge in the book).
In the first free-body diagram, I understand that m2g (directed down) is the force of gravity, and M2 (anticlockwise) is the externally applied torque. However I am unclear about F12x and F12y, which the book says are the "joint reaction forces at the pin joint".
(Similarly I am also unclear about the forces F12x, F12y, F23x and and F23y in the second free-body diagram).
I don't understand how the direction of the joint reaction forces is determined (eg why is F12x directed from left to right in both diagrams)?
Also, are these directions constant regardless of the orientation of the rod? Or will they change as the rod rotates?
Does anyone know of any references that deal with this topic (constructing free-body diagrams specifically for constrained rigid multibody dynamics -
particularly describing how to direct the joint reaction forces)? Any reference would be greatly appreciated, as I haven't been able to find an answer to this question so far online or in books.
Thanks for your help,
Nick.
I have been reading the book "Computational Dynamics" by Ahmed Shabana, and have a few questions.
The book talks about creating "free-body diagrams" for constrained rigid multibody dynamics problems.
I have attached two examples:
The first is a "pendulum with a moving base":
which is described in the book as:
"Body 1 is a slider block that has a specified motion defined by the function z(t). Body 2 is a uniform slender rod that has mass m2, mass moment of inertia about its centre of mass J2, and length l. The rod that is subjected to the external moment M2 is connected to the sliding block by a pin joint at O."
The second,
is described in the book as:
"The system consists of the ground denoted as body 1, a rod OA denoted as body 2, and a disk denoted as body 3. The rod is connected to the ground by a pin joint at O, while the disk is connected to the rod by a pin joint at A. The rod is assumed to be uniform and its length is l."
I have also attached the book's free-body diagrams for these two examples.
I'm unclear about how the free-body diagrams are constructed (and it is assumed knowledge in the book).
In the first free-body diagram, I understand that m2g (directed down) is the force of gravity, and M2 (anticlockwise) is the externally applied torque. However I am unclear about F12x and F12y, which the book says are the "joint reaction forces at the pin joint".
(Similarly I am also unclear about the forces F12x, F12y, F23x and and F23y in the second free-body diagram).
I don't understand how the direction of the joint reaction forces is determined (eg why is F12x directed from left to right in both diagrams)?
Also, are these directions constant regardless of the orientation of the rod? Or will they change as the rod rotates?
Does anyone know of any references that deal with this topic (constructing free-body diagrams specifically for constrained rigid multibody dynamics -
particularly describing how to direct the joint reaction forces)? Any reference would be greatly appreciated, as I haven't been able to find an answer to this question so far online or in books.
Thanks for your help,
Nick.