Why Can't I Use My Indicated Vector ds on a Gaussian Surface?
- Context: Graduate
- Thread starter logearav
- Start date
Click For Summary
SUMMARY
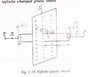
The discussion clarifies the correct application of the vector dS in relation to Gaussian surfaces in electromagnetism. It emphasizes that dS must always be perpendicular to the surface and directed outward for closed surfaces. The participants highlight that the flux must be calculated through all sides of the Gaussian surface, including the two caps and the cylindrical side. The electric field's orientation relative to dS is also crucial, as it determines whether the flux through a surface is zero.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Gaussian surfaces in electromagnetism
- Familiarity with vector calculus, particularly surface integrals
- Knowledge of electric fields and their properties
- Experience with flux calculations in physics
- Study the application of Gauss's Law in various geometries
- Learn about surface integrals in vector calculus
- Explore the relationship between electric fields and flux through surfaces
- Review examples of calculating flux through different Gaussian surfaces
Students of physics, educators teaching electromagnetism, and anyone seeking to deepen their understanding of Gaussian surfaces and electric field interactions.
Similar threads
- · Replies 9 ·
Undergrad
How to choose Gaussian surface
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
- · Replies 22 ·
- · Replies 2 ·
Undergrad
Pushing a rod in a magnetic field
- · Replies 15 ·
- · Replies 5 ·
- · Replies 1 ·
Undergrad
When is a water surface not dispersive?
- · Replies 1 ·