Emilio_2004
- 6
- 0
- TL;DR
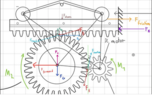
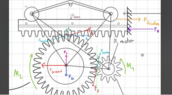
- I want to build a monorack system but i struggle to understand the mechanical basics. What forces and torques act on a gear on a fixed rack
I am confused cause in my diagram for the sake of simplicity i ignore gravity and friction. But the net torque on the gear is zero? How can that be? I am sorry if thats a stupid question but i am just a bit confused and honestly stuck since days on that.
F react. Is the force that causes the gear to move forward cause on the free body diagram of the gear thats the net force. We apply a torque to the gear. This will result in a tangential force at the point of contact. Of course we need to also consider the pressure angle of the mashing, thats why i drew a force pointing upwards on from bearing of the gear to account for that (same for the rack) The force from the gear is the same as the one that will be acting on the rack (actio reactio).
The rack experiences a net force of zero as its fixed into place. But my free body diagram as it is now doesn’t make sense cause of what i already said regarding the net torque. I already was on Reddit and i got a response stating that the normal force on the gear/ the reaction force gets smaller by time, but I honestly dont get it, i hope someone can help me out. I also apologize if i am a bit unclear with what i wrote so far.
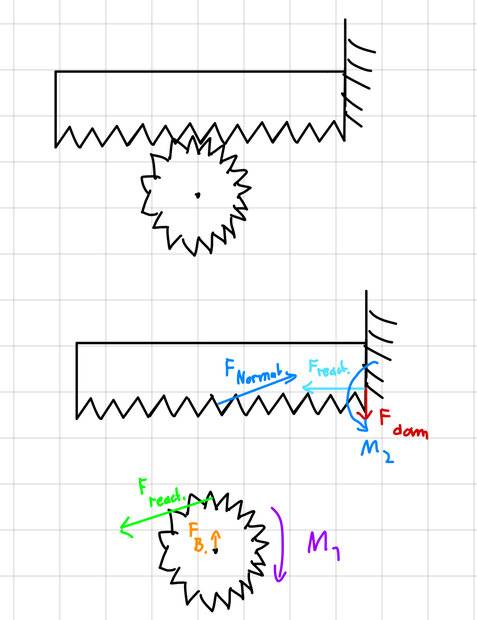
F react. Is the force that causes the gear to move forward cause on the free body diagram of the gear thats the net force. We apply a torque to the gear. This will result in a tangential force at the point of contact. Of course we need to also consider the pressure angle of the mashing, thats why i drew a force pointing upwards on from bearing of the gear to account for that (same for the rack) The force from the gear is the same as the one that will be acting on the rack (actio reactio).
The rack experiences a net force of zero as its fixed into place. But my free body diagram as it is now doesn’t make sense cause of what i already said regarding the net torque. I already was on Reddit and i got a response stating that the normal force on the gear/ the reaction force gets smaller by time, but I honestly dont get it, i hope someone can help me out. I also apologize if i am a bit unclear with what i wrote so far.