- #1
sevensixtwo
- 4
- 0
Phi ~ 1.618
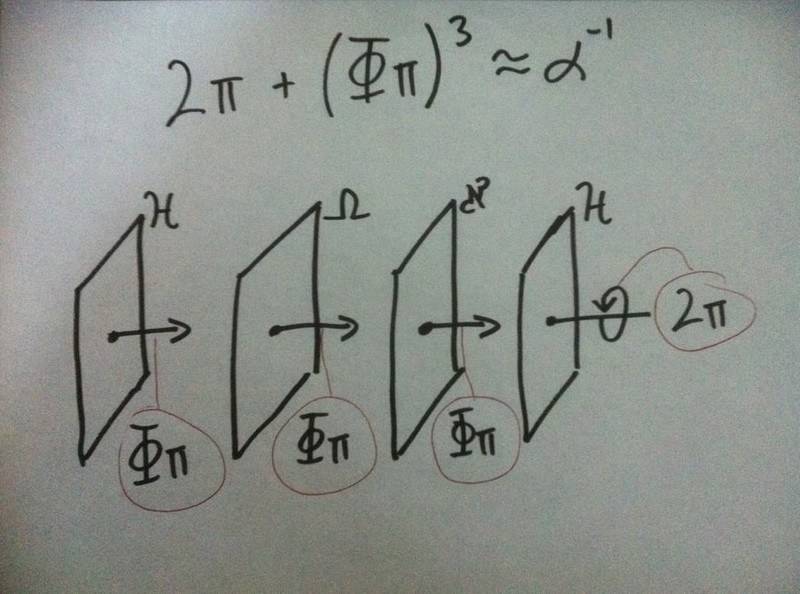
The Fine Structure Constant, denoted by α, is a dimensionless number that characterizes the strength of the electromagnetic interaction between elementary particles. It is approximately equal to 1/137 and is a fundamental constant in physics.
The Geometric Interpretation of Fine Structure is a theoretical framework that attempts to explain the value of the Fine Structure Constant by relating it to the geometry of space-time. It suggests that the value of α is determined by the number of dimensions of the universe and the curvature of space-time.
The Fine Structure Constant is significant because it governs the strength of the electromagnetic interaction, which is responsible for many fundamental forces and processes in the universe. It also plays a key role in the study of particle physics and cosmology.
The Fine Structure Constant was first calculated by physicist Arnold Sommerfeld in 1916 using the Rydberg formula, which describes the spectral lines of hydrogen atoms. He found that the value of α was approximately 1/137, which was later confirmed by other experiments and calculations.
Yes, the value of the Fine Structure Constant has been measured with increasing accuracy over the years through various experiments and calculations. The most recent measurements put its value at approximately 1/137.035999206. However, there is still ongoing research and debate about the exact value and its possible variations.