Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around sizing a motor for linear motion, particularly focusing on the time versus distance graph when the stroke is very short. Participants explore the implications of short strokes on motor performance, feedback loops, and precision in positioning applications.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Mathematical reasoning
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
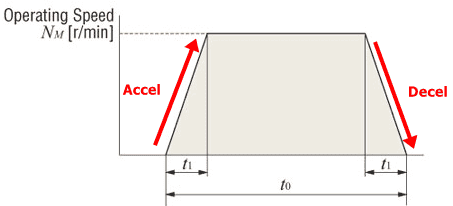
- One participant inquires about the shape of the time-distance graph for a short stroke of 0.5 mm, with a velocity of 0.1 m/s and acceleration of 1 m/s².
- Another participant suggests that the motor's inertia and feedback loop characteristics are crucial for performance in such applications.
- A participant proposes using a piezo transducer for fine position corrections.
- One participant describes a method of sketching acceleration, velocity, and position to visualize the motion, starting with constant acceleration and calculating necessary parameters.
- There is a question regarding the formula used for distance, specifically whether it should be Distance = 0.25 * a * t² instead of Distance = 0.5 * a * t².
- Participants discuss the integration of acceleration to derive velocity and position, noting the discontinuities in the acceleration curve and their implications for motion control.
- Clarifications are made on how to derive the acceleration value of 0.8 m/s² using the distance and time parameters provided.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express various viewpoints on the calculations and methods for analyzing motor performance in short stroke applications. There is no consensus on the correct formula for distance or the best approach to achieve precision in motion control.
Contextual Notes
Participants acknowledge the importance of understanding motion control concepts and the role of diagrams in communicating these ideas, especially in complex engineering scenarios. The discussion highlights the need for clarity in mathematical steps and assumptions when analyzing motor performance.