Purpleshinyrock
- 27
- 6
Poster has been reminded to show their work on schoolwork problems
- Homework Statement
- I need help understanding this exercise
- Relevant Equations
- dont know
Hello. Can someone tell me what area of phisics should I study to better understand this exercise( I ve been looking at kinematics since it asks for the velocity but I can't seem to find where it talks about different points like this) and also what should I do to solve this exercise please?
A sled with a mass equal to 100 kg departs from rest at point 1 ( h 1 = 12.2 m) and descends figure ramp, without friction.
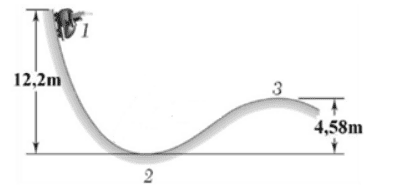
What is the speed of the sled when it reaches point 3, at a height h 3 = 4.58m?
(Use g = 10.0 m ∙ s -2 ).
□ (A) v 3 = 6.77 m ∙ s -1
□ (B) v 3 = 8.73 m ∙ s -1
□ (C) v 3 = 12.35 m ∙ s -1
□ (D) v 3 = 15.62 m ∙ s -1
□ (E) v 3 = 152.40 m ∙ s -1
A sled with a mass equal to 100 kg departs from rest at point 1 ( h 1 = 12.2 m) and descends figure ramp, without friction.
What is the speed of the sled when it reaches point 3, at a height h 3 = 4.58m?
(Use g = 10.0 m ∙ s -2 ).
□ (A) v 3 = 6.77 m ∙ s -1
□ (B) v 3 = 8.73 m ∙ s -1
□ (C) v 3 = 12.35 m ∙ s -1
□ (D) v 3 = 15.62 m ∙ s -1
□ (E) v 3 = 152.40 m ∙ s -1
Last edited by a moderator: