SUMMARY
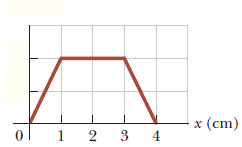
This discussion clarifies the relationship between electric potential (V) and electric field direction along the x-axis. A negative slope in the V(x) graph indicates that the electric field points in the positive x-direction, while a positive slope indicates that the field points in the negative x-direction. The participants explore the implications of this relationship using examples such as concentric conducting spheres and the behavior of positive test charges in varying potential fields. Ultimately, the electric field direction is defined as the negative gradient of the potential slope.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric potential (V) and electric field concepts
- Familiarity with the relationship between slope and field direction
- Knowledge of charge distributions and their effects on electric potential
- Basic grasp of graphical analysis in physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the mathematical relationship between electric potential and electric field using calculus
- Explore the concept of equipotential surfaces and their relation to electric fields
- Investigate the behavior of electric fields around different charge distributions, such as point charges and dipoles
- Learn about the implications of electric potential in practical applications, such as capacitors and electric circuits
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, educators teaching electromagnetism, and anyone interested in understanding the principles of electric potential and electric fields.